


Nutrients
7N
Why it is needed?
Nitrogen (N)
Needed for the formation of all plant and animal proteins
What happens without it?
X
Causes stunted and spindly plants, low protein content in seed and vegetative parts, and fewer leaves
15P
Why it is needed?
Phosphorus (P)
Vital for
plant photosynthesis
What happens without it?
X
Causes stunted growth, reduced crop yields, low quality harvests and moisture stress
19K
Why it is needed?
Potassium (K)
Essential for robust high quality crops
What happens without it?
X
Causes slower growth, delayed pollination and maturity, overdeveloped leaves, reduced crop yields, weakened stalks and moisture stress
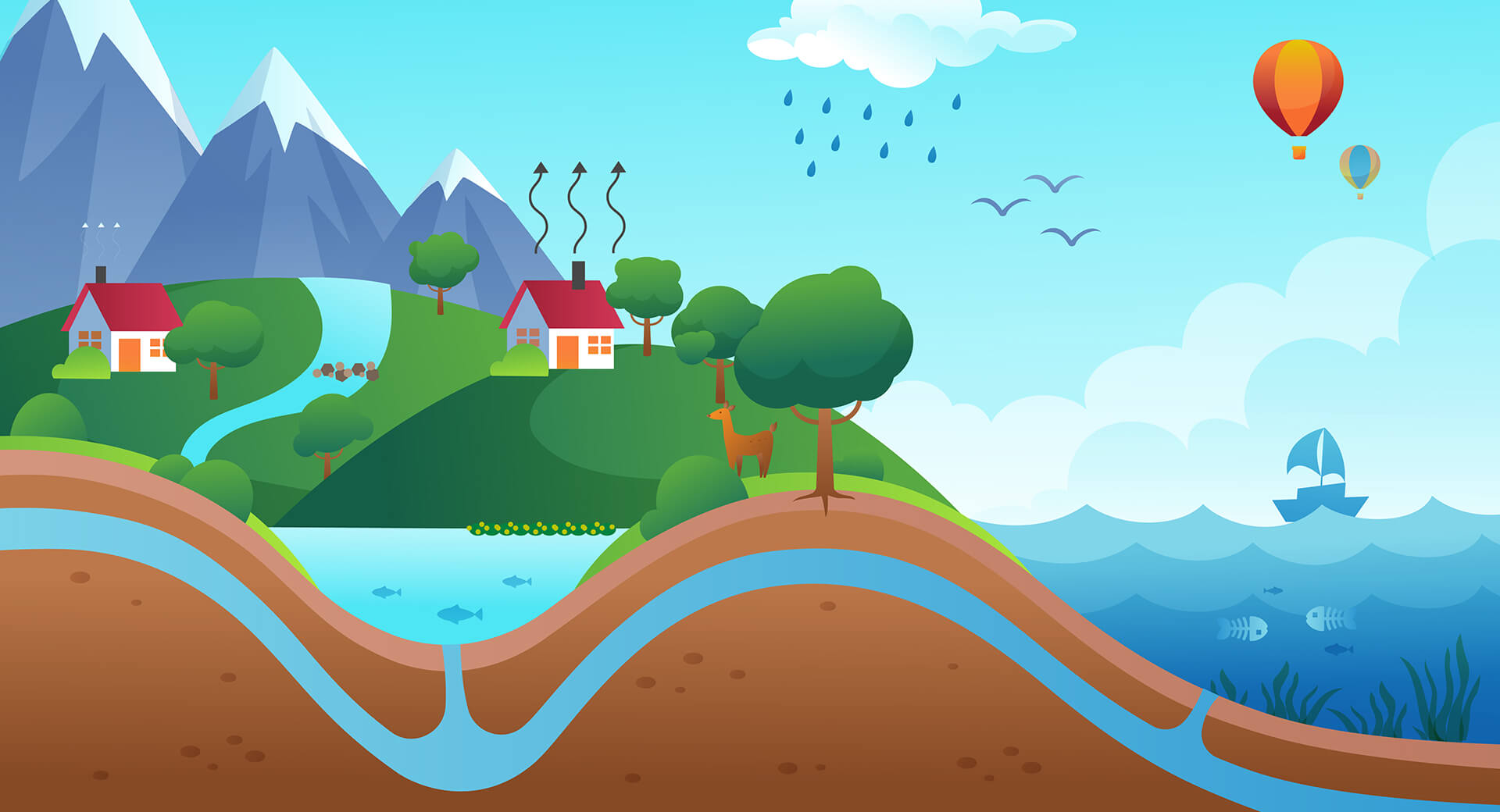
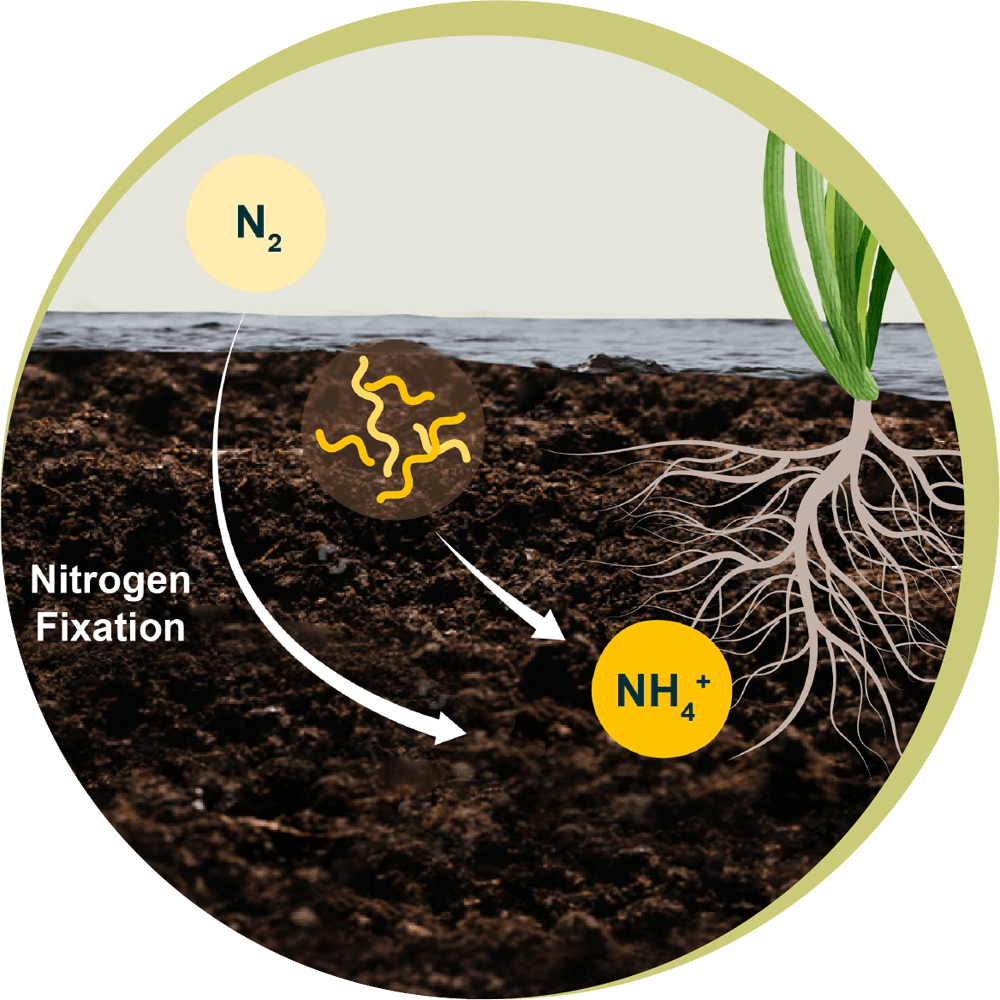
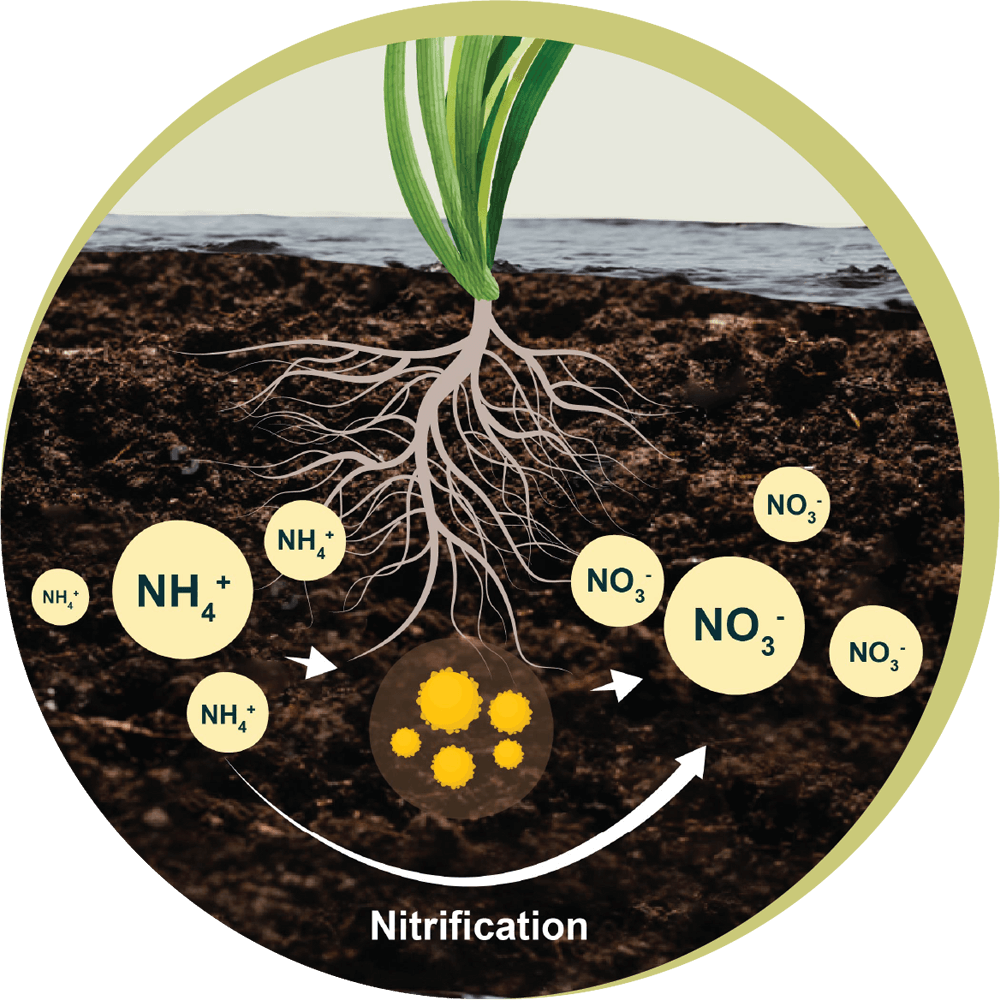
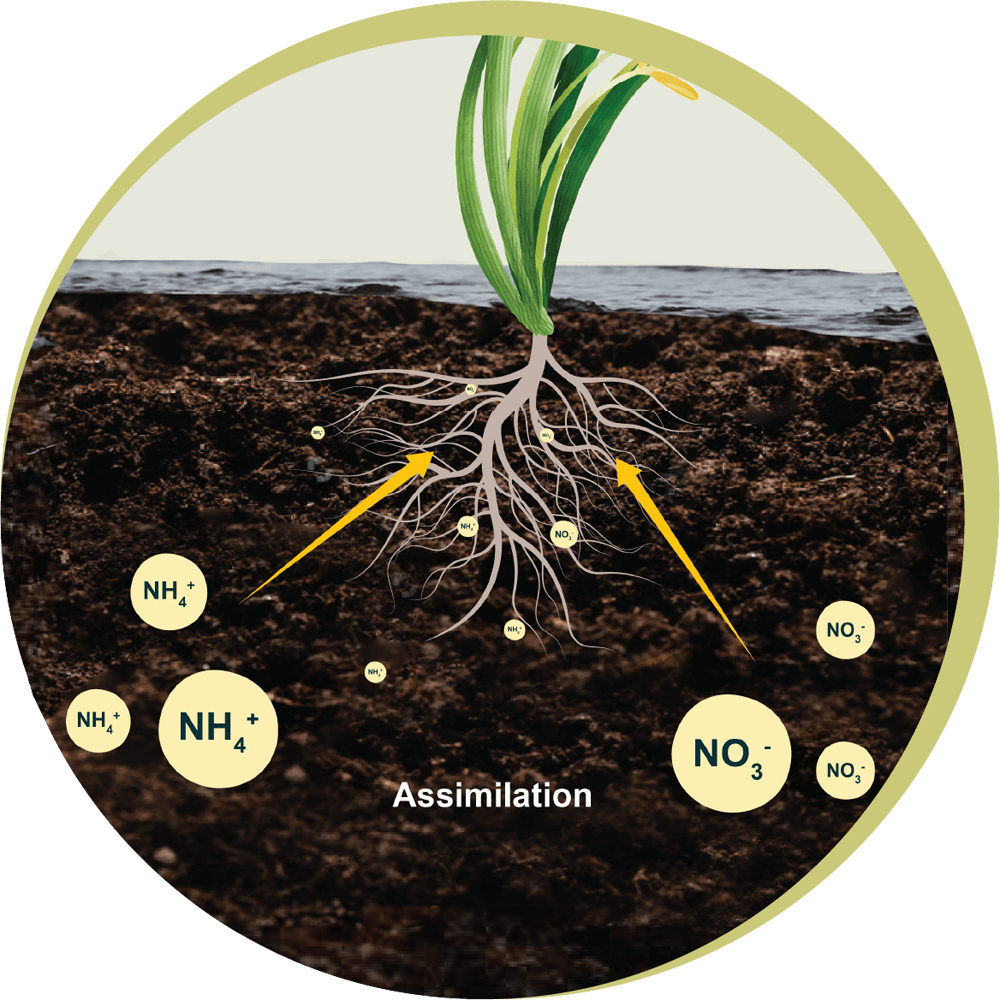
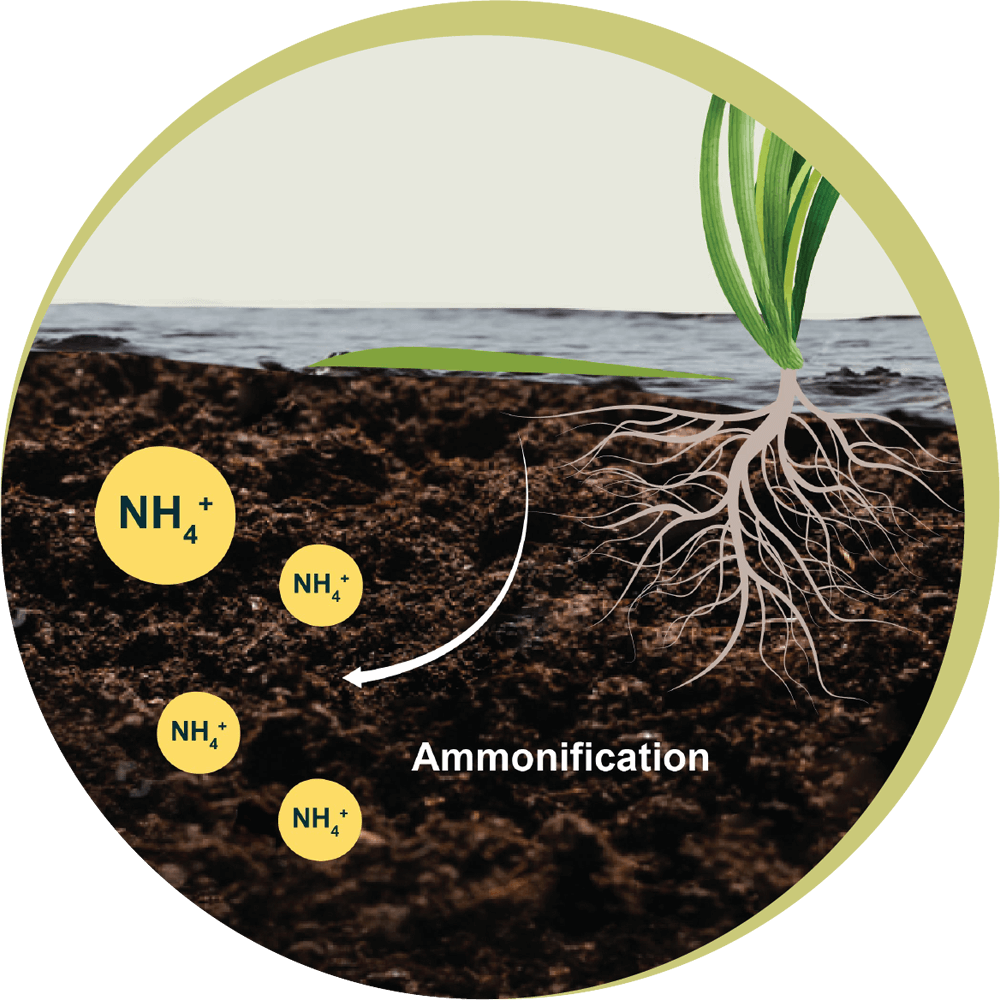
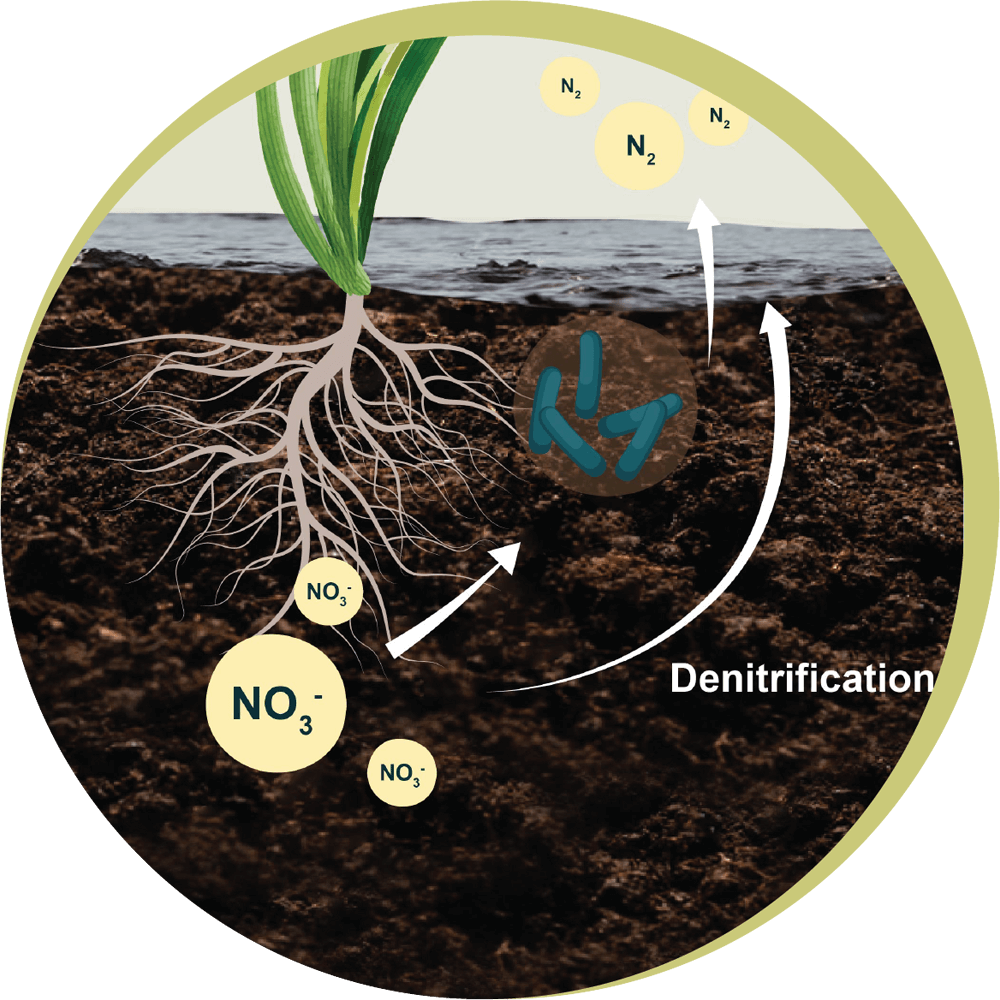
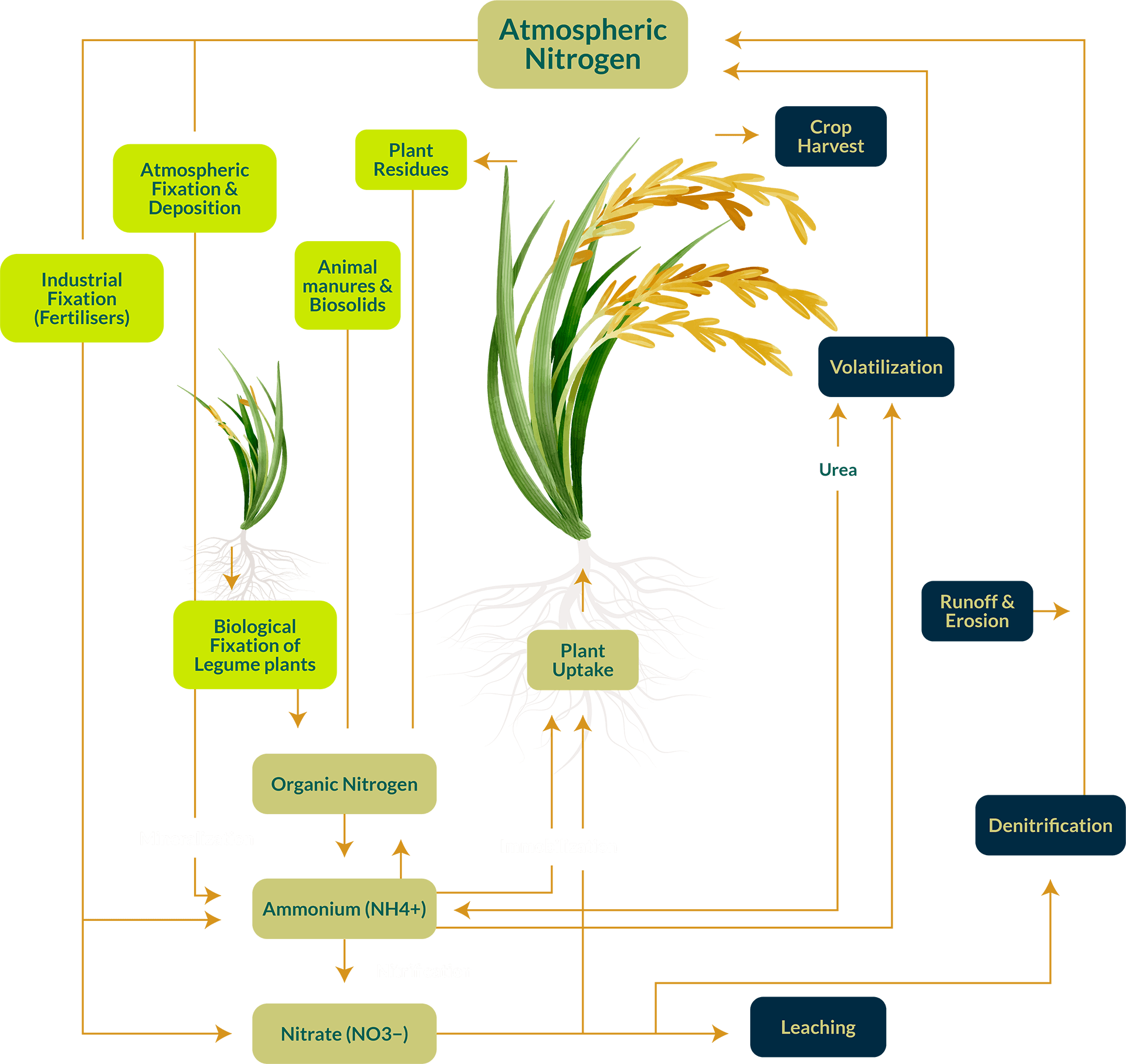
Diagram of The
Nitrogen Cycle
Component
Input to soil
Loss from soil
Environmental
Impact
Fertilizers boost crop growth, but they pose environmental challenges.